Transgenic Plants And Animals Wikipedia
Transgenic plants and animals Transgenic plants are plants that have been genetically engineered a breeding approach that uses recombinant DNA techniques to create plants with new characteristics.
Transgenic plants and animals wikipedia. Transgenic plants potato and cotton were for the first time made available to farmers in USA. The cell uses CO 2 water minerals and sun light to synthesise thousands of valuable and complex products which are the basis of animals life. Transgenic animals for the production of therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are produced by transferring fertilized transgene-carrying embryos to recipient animals.
By the year 1998-99 five major transgenic crops cotton maize soybean canola and potato were in widespread use. Transgenic Plants as Bioreactor Molecular Farming. Contents Transgenic animals are more widely used for various purposes.
The monoclonal antibodies peptide hormones cytokinins and blood plasma proteins are being produced in transgenic plants and their parts such as tobacco in leaves potato in tubers sugarcane in stems and maize in. Applications of animal transgenesis may be divided into three major categories. These genes are passed on to the successive generations.
A transgenic plant contains a gene or genes that have been artificially inserted. Although several recombinant proteins used in medicine are successfully produced in bacteria some proteins require a eukaryotic animal host for proper processing. A foreign gene will be inserted into a plant of a different species or kingdom.
Plant cells act as the Natures cheapest factory. Transgenic plants are also called Genetically modified crops. For this reason the desired genes are cloned and expressed in animals such as sheep goats chickens and mice.
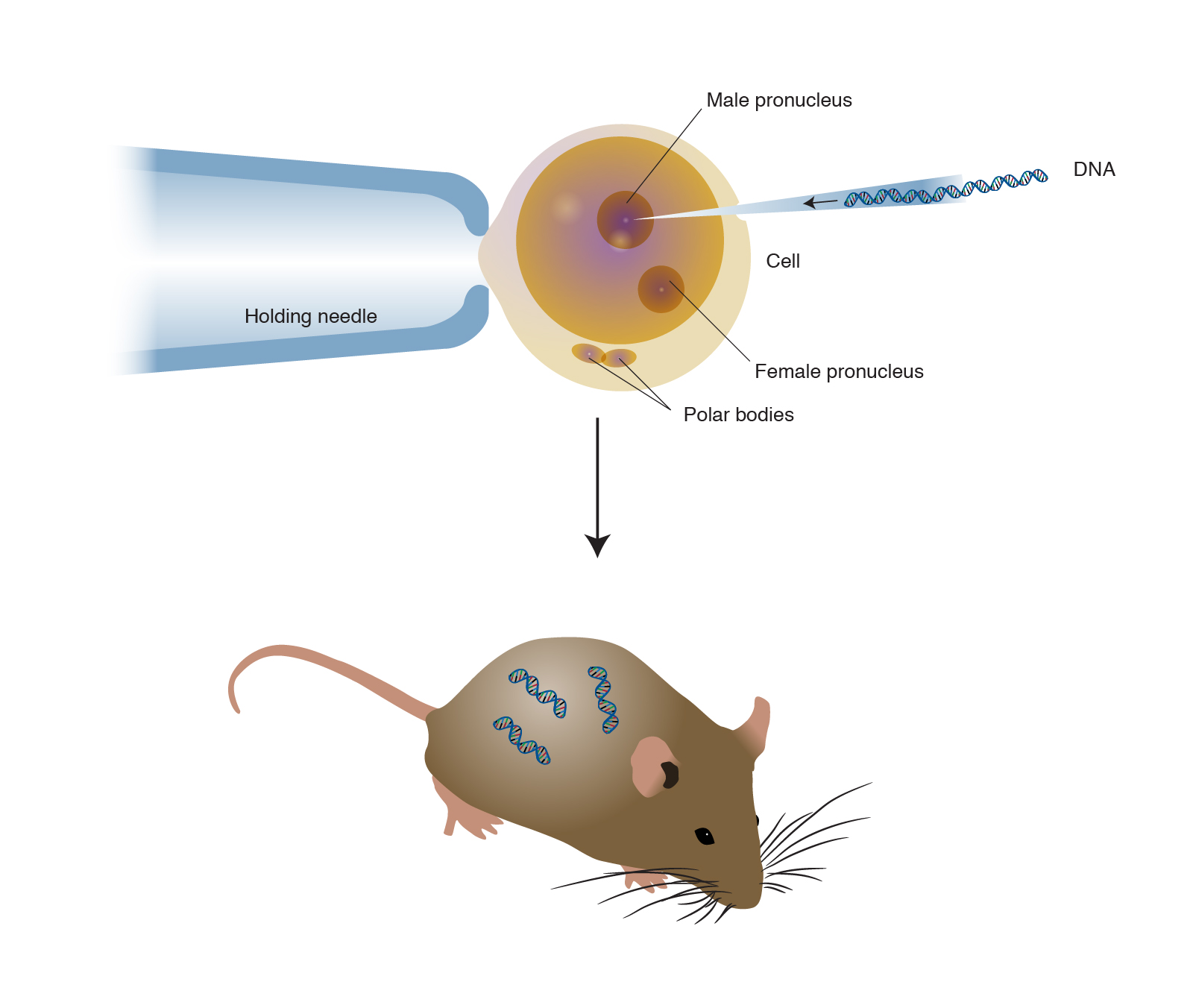
Following natural gestation and birth offspring are subject to tissue biopsy and blood sampling. Transgenesis is the phenomenon in which a foreign gene with desired characteristics is introduced into the genome of the target animal. The aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species.