Transgenic Animals Definition Biology

Transgenic animals are also becoming useful commercially.
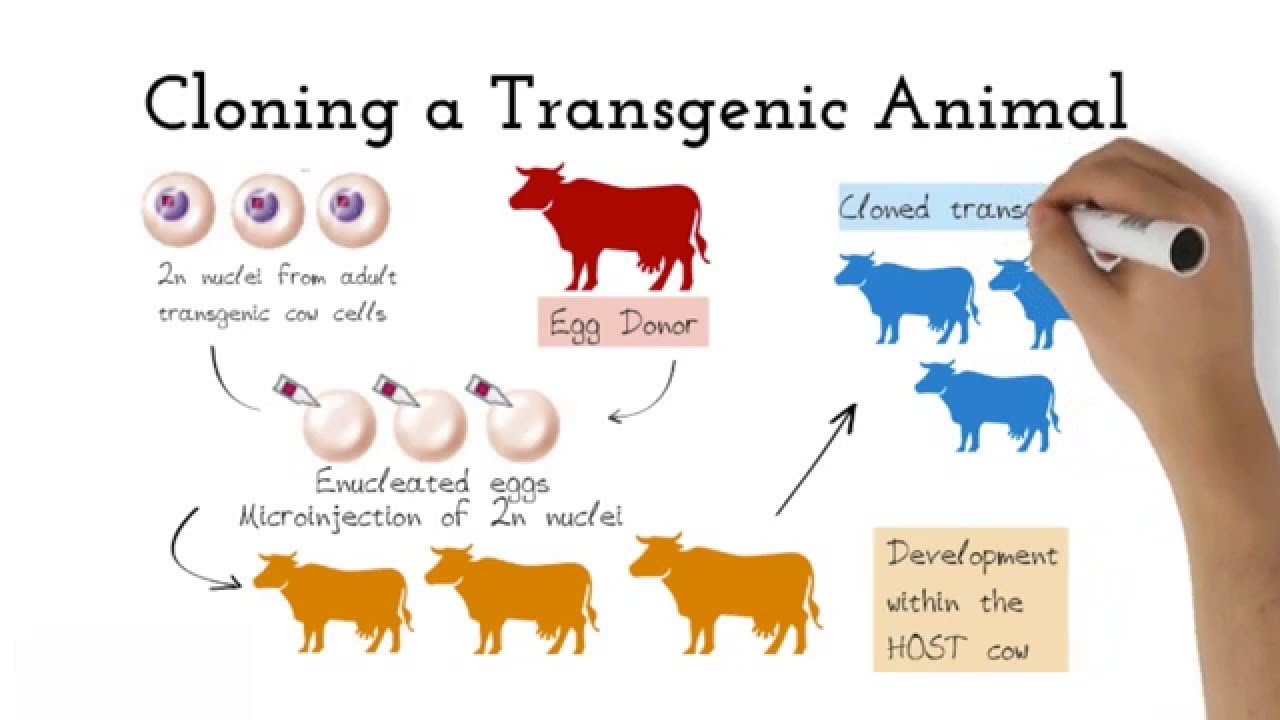
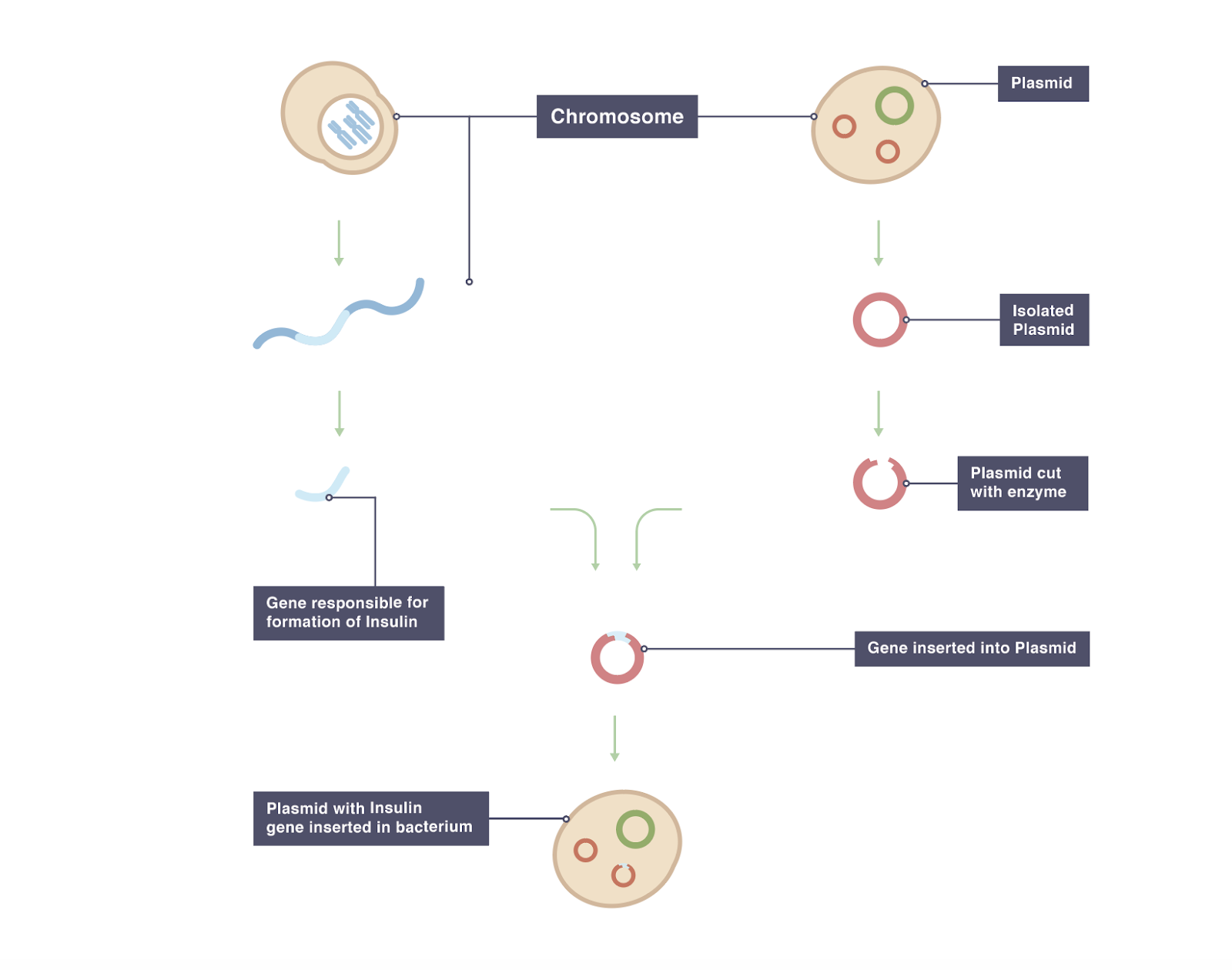
Transgenic animals definition biology. Full article A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been changed to carry genes from other species. Transgenic means that one or more DNA sequences from another species have been introduced by artificial means. The foreign DNA or transgene that is transferred to the recipient can be from other individuals of the same species or even from unrelated species.
They are then exposed to the toxic substances and the effects studied. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. In addition to the gene.
The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. In addition to the gene itself the DNA usually includes other sequences to enable it. A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been altered by the transfer of a gene or genes from another species or breed.
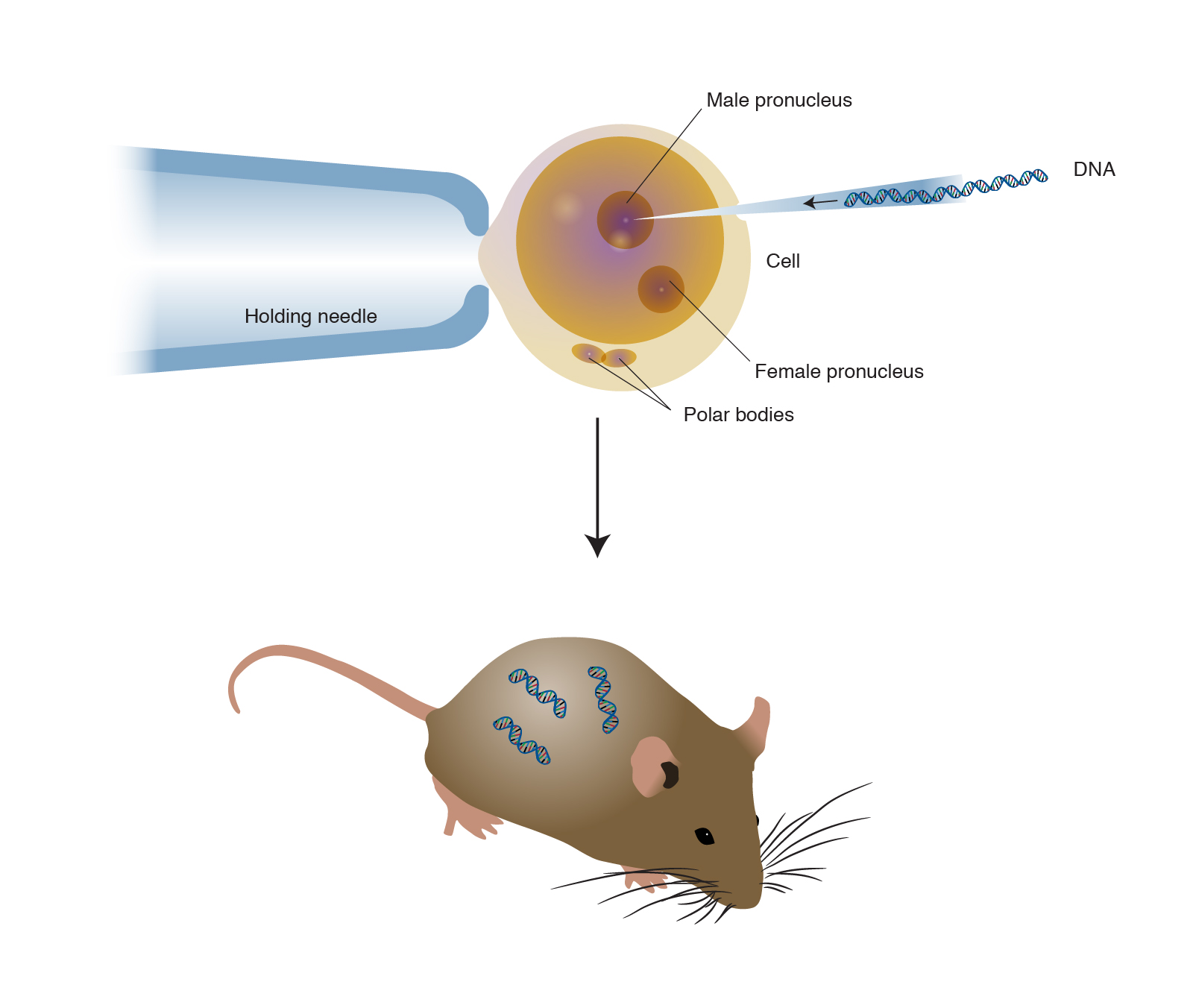
Animals usually are made transgenic by having a small sequence of foreign DNA injected into a fertilized egg or developing embryo. BTransgenic animals are made that carry genes which make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals. Human transplant organ arising from an animal.
The term transgenic animal refers to an animal in which there has been a deliberate modification of the genome - the material responsible for inherited characteristics - in contrast to spontaneous mutation FELASA September 1992 revised February 1995. They may also be engineered to have advantageous or useful traits. Arise from pluripotent stem cells.
Transgenic animal genetically engineered animalor offspring of genetically engineeredanimals. Transgenic animal industrial applications 3 chemical safety testing toxicity-sensitive transgenic animals animal bioreactor protein production. Transgenic plants can be made by introducing foreign DNA into a variety of different tissues.

_1602913203_391831-5.jpg)